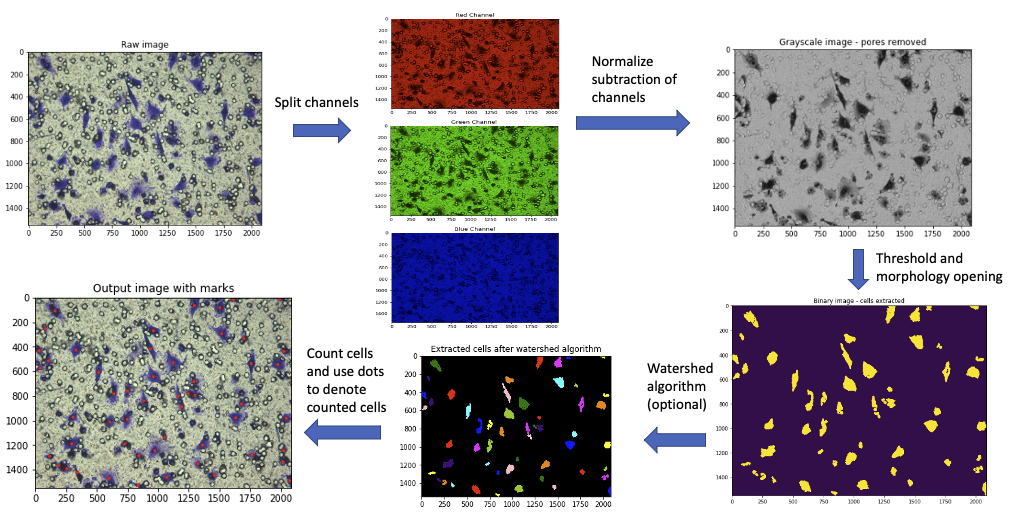
Project MONAI (Medical Open Network for AI) is an open-source framework that accelerates research and clMedSpaCy is a powerful library built specifically for clinical natural language processing (NLP) using the popular SpaCy framework. Designed to handle the unique complexities of clinical text, MedSpaCy provides specialized tools that allow healthcare providers and researchers to analyze medical data more efficienThe Automatic Cell Counter is a versatile algorithm designed to count cell numbers in 2D microscopy images, particularly from the Boyden Chamber assay, which is commonly used to study cell migration and invasion. This tool, implemented in Python 3.9, includes a user interface that allows manual correction, ensuring accurate cell counts even in densely populated or complex regions. The algorithm automatically identifies cell centers using red dots, highlights areas that may require closer attention, and supports easy, interactive adjustments by the user.
Key Features
- Automated Counting: Detects and marks cell centers in microscopy images.
- User-Friendly Interface: Allows manual corrections with interactive controls.
- Highlighting Critical Regions: Marks high-density regions and possible cell overlaps for review.
- Excel Output: Generates an Excel file with initial and corrected cell counts for easy data analysis.
How It Works
After loading each image, red dots indicate detected cells, while green dots and red bounding boxes mark high-density areas or potential split cells. Users can adjust dots as needed and save the updated counts by pressing ‘d’ (Done) on the keyboard. Final results are saved in an Excel file for both automatically detected and manually adjusted counts.
Cell Images
This tool is optimized for images from Boyden Chamber assays captured under a microscope at 20x magnification. Adjustments may be required for different image sizes.