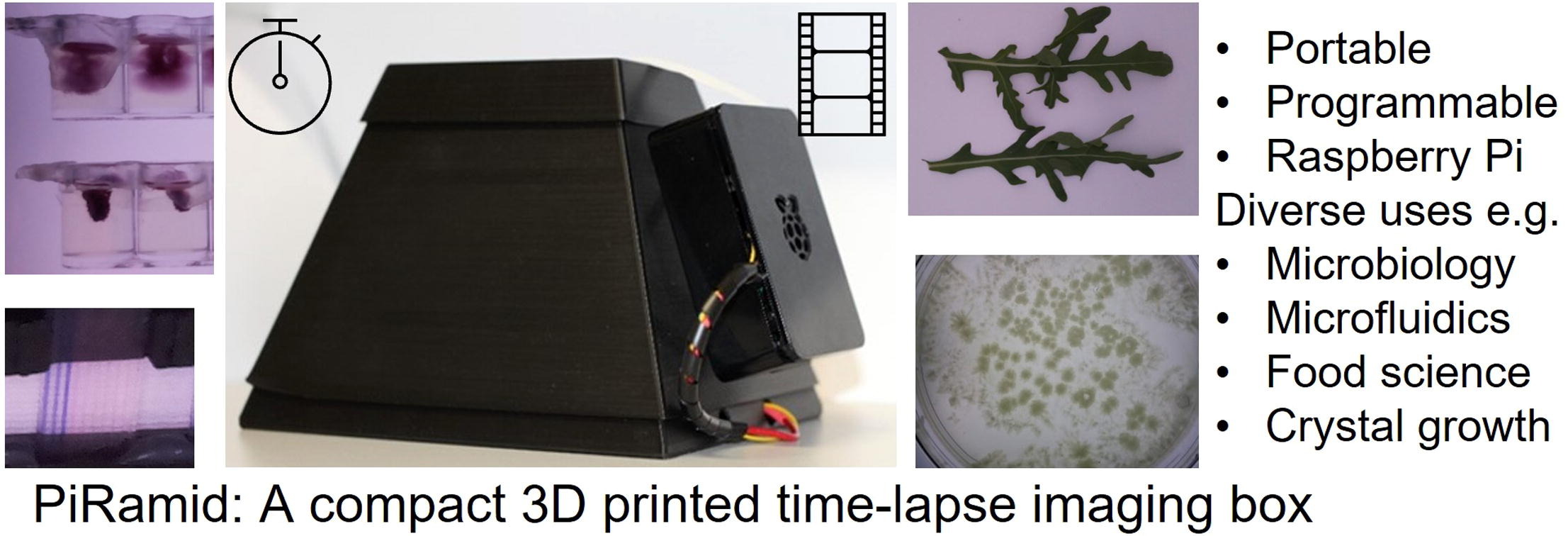
The PiRamid is a compact, portable, and cost-effective imaging device developed using the Raspberry Pi platform. It is designed to automate small-scale time-lapse digital analysis, making it suitable for both laboratory and field use.
Key Features:
- Modular Design: The PiRamid features a three-piece 3D-printed structure that allows for easy integration of different camera systems and lighting configurations, such as single-wavelength LEDs for fluorescence imaging. Centaur
- Controlled Illumination: Its enclosed design ensures complete control over lighting conditions, enhancing image quality compared to conventional cameras or smartphones used under ambient lighting. Centaur
- Automation: Utilizing Python scripts, the PiRamid automates illumination and image capture processes, facilitating time-lapse imaging for various experiments. Centaur
Applications in Immunology Diagnostics:
While the PiRamid is not a standard tool in routine immunology diagnostics, it offers potential benefits in specific areas:
- ELISA Monitoring: The device can be employed to monitor colorimetric changes in enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA) over time, providing quantitative data on antigen-antibody interactions. Centaur
- Cell Culture Observation: It can capture time-lapse images of cell cultures, aiding in the assessment of cell proliferation, morphology, and response to immunological stimuli. Centaur
- Research and Development: The PiRamid is valuable in research settings for developing and validating new immunological assays, especially where time-lapse imaging is crucial. Centaur
Limitations:
Despite its versatility, the PiRamid may not replace specialized equipment required for certain immunology tests, such as flow cytometers or automated immunoassay analyzers. Its application is more suited to research and specific diagnostic scenarios rather than routine clinical diagnostics.
In summary, the PiRamid offers a flexible and affordable imaging solution that can enhance certain aspects of immunology diagnostics, particularly in research and development contexts. However, it is not a direct substitute for specialized equipment used in standard immunology diagnostic tests.